Molecular Screening for Environmental Side-Effects
Testing of Active Substance Precursors for Environmental Effects
Active substances of pesticides, biocides, drugs or cosmetics are deployed to the ecosystem either in a targeted manner or via their application to humans. Thereby, these substances can exert far-reaching adverse effects on non-target organisms. The ecological risk assessment of a continuously growing number of newly developed active substances represents a significant cost factor for the chemical industry. Moreover, the OECD-tests demanded by the regulatory authorities are time-consuming and intensive in resources, rendering them incompatible with a screening of substance precursors under development.
OMICs
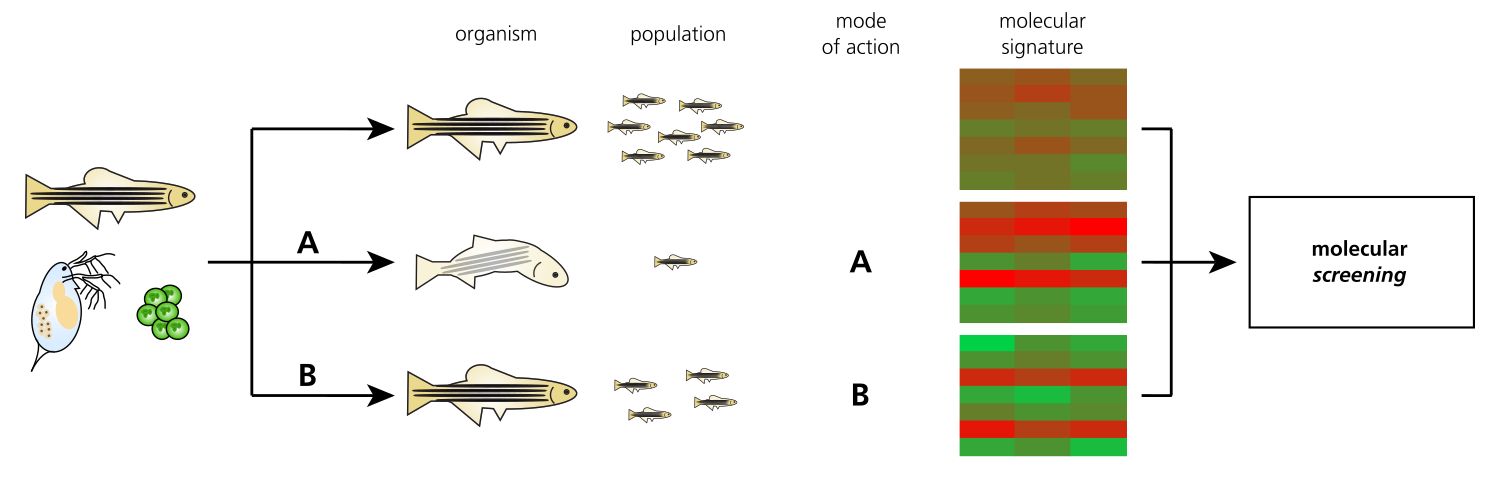
The application of recent OMICs methodology allows for a sensitive and genome-wide identification of substance-induced molecular changes in ecologically relevant organisms at the levels of DNA (Epigenome), RNA (Transcriptome) and proteins (Proteome). Moreover, such systems biology investigations need minimal resources, making them a promising approach for the early identification of environmental effects of substance precursors in the scope of a screening. In the same time, OMICs methods allow for a significant reduction in the number of animal tests. A deep knowledge about the substance-induced molecular changes and their direct linkage with phenotypes and population effects will facilitate an early identification of ecotoxic substances and the classification of substances regarding their environmental effects.
Adverse Outcome Pathways (AOPs)
The OMICs-based identification of pathways, which are perturbed by a specific substance, significantly contributes to the establishment of Adverse Outcome Pathways (AOPs). The AOP concept was developed to directly link molecular initiating events (MIEs) to the resulting adverse effects to the organism and the population and is increasingly gaining attention also by the regulatory authorities.
Fraunhofer Attract „Eco’n’OMICs“
The Fraunhofer Attract Group „Eco’n’OMICs“ combines ecotoxicological approaches with OMICs methodology (RNA-Seq, quantitative LC-MS/MS) in order to generate a data base of substance-specific early molecular changes preceding adverse effects on the organism and the population. These molecular fingerprints will be used to develop screening approaches for the environmental risk prediction of substance precursors under development. The availability of such a screening for environmental side-effects already during early substance development will avoid the costly development of substance precursors with a high ecotoxicological potential and will allow for a sustainable development of environmentally safe active substances.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Molecular Biology and Applied Ecology IME
Fraunhofer Institute for Molecular Biology and Applied Ecology IME